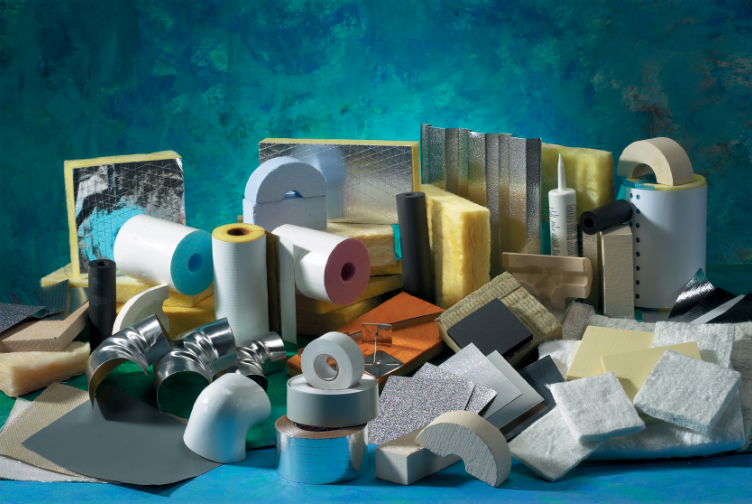
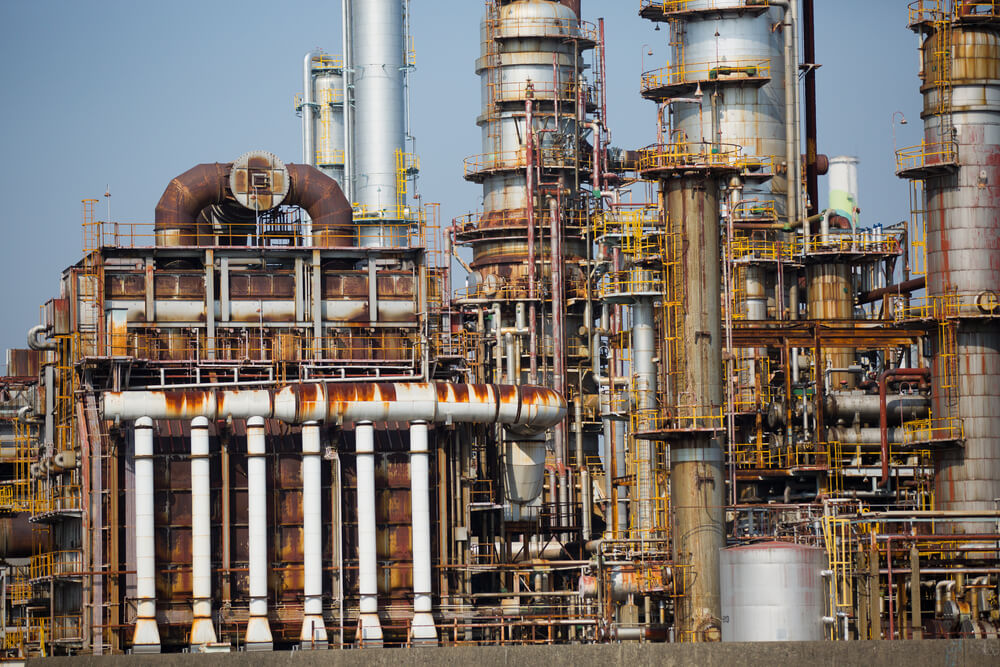
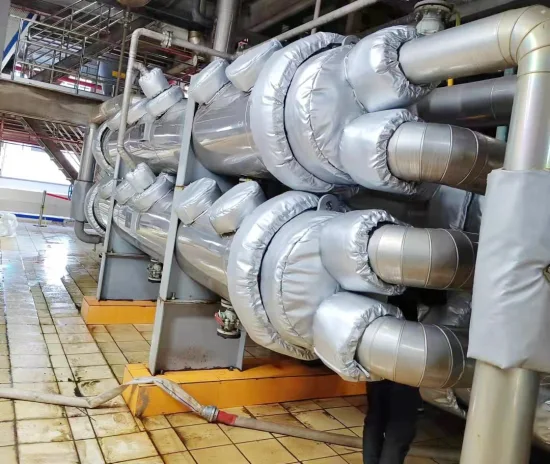
In today’s world, purchasing insulating materials is considered one of the most critical decisions in industrial and construction projects. The correct choice of insulation material not only affects energy efficiency and reduces operational costs but also plays a key role in the safety and longevity of equipment.
Table of Contents
- Types of Insulating Materials and Applications
- Factors Influencing the Choice of Insulation
- Guide to Buying Insulating Materials
- Important Tips for Purchasing
- Pricing and Budgeting
Types of Insulating Materials and Applications
1. Fibrous Insulation
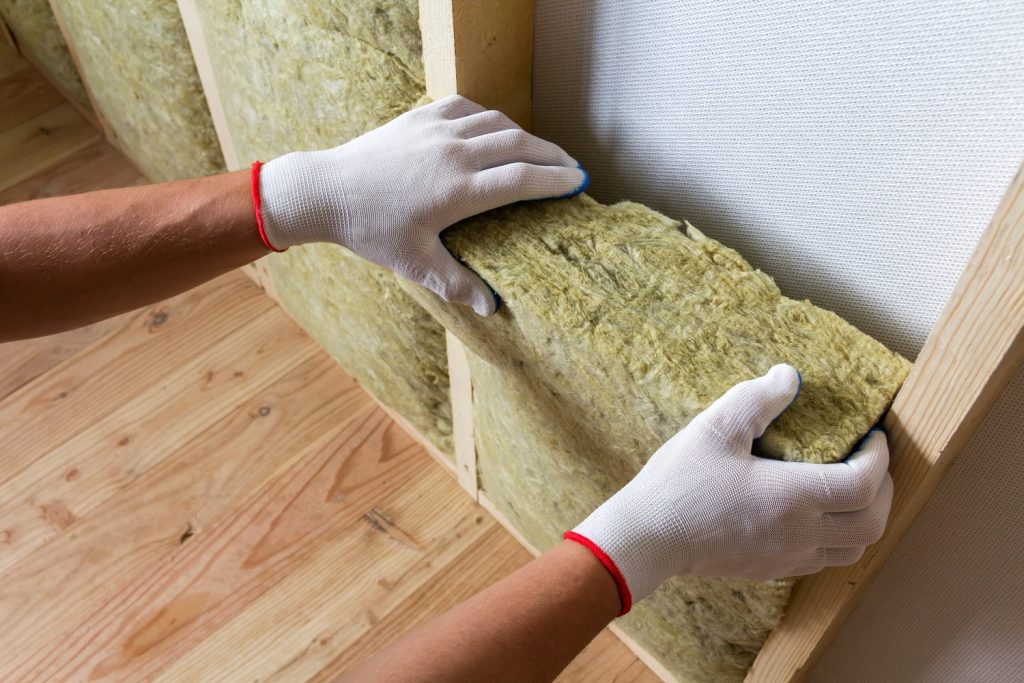

Rock Wool
Rock wool insulation is one of the most widely used insulating materials in various industries. This material is produced from molten volcanic rocks and possesses unique properties:
Advantages of Rock Wool:
- High thermal resistance (up to 1000°C)
- Fire resistance
- Excellent sound insulation properties
- Moisture resistance
- Eco-friendly
Applications of Rock Wool:
- Insulation of walls and ceilings
- Insulation of pipes and industrial equipment
- Turbine insulation and power plant equipment
- Insulation of furnaces and thermal equipment
Fiberglass
Fiberglass is produced by melting glass and transforming it into fine fibers. This material is a popular choice in the market due to its affordable price and good insulating properties.
2. Ceramic Insulation

Ceramic insulations are made from materials resistant to extremely high temperatures and are used in the petrochemical, steel, and glass industries:
Types of Ceramic Insulation:
- Ceramic Fiber
- Ceramic fire bricks
- Ceramic blankets
- Fiberglass fire-resistant mesh
3. Foam Insulation
Foam insulations include various types of polyurethane, polystyrene, and other polymeric materials produced in foam form.
Advantages of Foam Insulation:
- Easy installation
- Uniform coverage
- Moisture resistance
- Low weight
Factors Influencing the Choice of Insulating Materials
1. Temperature Conditions
Selecting the most suitable insulation depends on the application’s temperature range:
- Low temperatures (below 100°C): Fiberglass, polymer foams
- Medium temperatures (100-650°C): Rock wool, mineral insulations
- High temperatures (above 650°C): Ceramic fibers, fire bricks
2. Application Environment
Dry: Most insulations are usable
Humid: Moisture-resistant insulations like closed-cell foams
Corrosive: Chemical-resistant insulations
3. Safety Standards
- UL 1709 Standard: For fireproof insulation
- ASTM Standard: For material technical specifications
- ISO Standard: For quality and performance
Guide to Buying Insulating Materials
Step 1: Needs Analysis
Before making a purchase, you must carefully analyze your needs:
- Determine the operational temperature range
- Calculate the required area
- Assess environmental conditions (humidity, chemicals)
- Define the available budget
Step 2: Selecting the Insulation Type
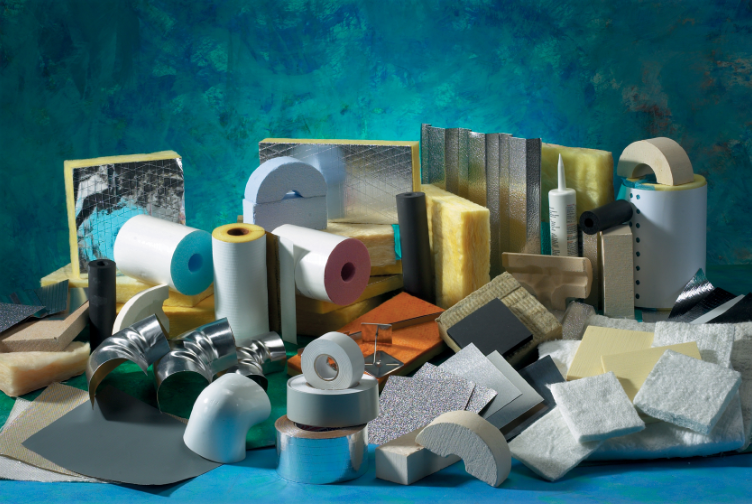

Based on the needs analysis, select the most suitable type of insulation:
For Industrial Applications:
- Jacket thermal insulation for equipment
- Pillow-type insulation for complex areas
- Welding blanket for temporary protection
For Construction Applications:
- Board rock wool for walls
- Roll rock wool for ceilings
- Foam insulations for specific spaces
Step 3: Reviewing Technical Specifications
Important Parameters:
- Thermal Conductivity Coefficient (K-Value), Thermal Resistance (R-Value), Density, and Thickness are among the most important technical parameters in selecting an insulating material.
- Fire resistance
Step 4: Selecting a Supplier
Choosing a reputable supplier is one of the most critical factors for project success:
Supplier Selection Criteria:
- In addition to industry history and experience, product quality, after-sales service, and competitive pricing, along with access to a variety of products, are the most important criteria for choosing a suitable supplier. Klevers Aryana Company is considered one of the most reputable manufacturers of these materials in Iran.
Golden Tips for a Smart and Optimal Purchase
1. Accurate Calculation: The Key to Preventing Resource Waste
Before taking any action, prevent extra costs and material waste by accurately calculating the required amount. This ensures your project proceeds without interruption and within an optimized budget. For this purpose, you can use the simple formula below:
Final Amount = Total Area × Required Thickness × Waste Factor (10-15%)2. Proper Storage: Protecting Your Investment
The quality of insulating materials is highly dependent on their storage conditions. To maintain maximum efficiency, ensure your warehouse is a dry environment with proper ventilation and protect the materials from direct sunlight, moisture, and any contamination. This guarantees the useful life and performance of the insulation.
3. Strategic Purchase Timing
The insulation materials market also has its peak and off-peak seasons. Typically, in autumn and winter demand and prices are higher due to an increase in construction projects. In contrast, spring and summer can be a golden opportunity to buy at more reasonable prices and better terms. Smart planning can lead to significant savings.
4. Choosing the Purchase Scale: Bulk or Retail?
The decision between bulk and retail purchasing is a strategic choice. Bulk purchasing comes with advantages like a lower unit cost, ensuring uniform quality for the entire project, and receiving special services. On the other hand, retail purchasing for smaller projects, offers greater flexibility, reduces warehousing costs, and allows for product testing before placing a large order. Assess your project’s needs and choose the best option.
Project Financial Management: From Pricing to Complete Budgeting
Understanding Price-Determining Factors
The final price of insulating materials is influenced by a set of key factors. The type of insulating material, the quality and brand reputation, the purchase volume (bulk or retail), **current market conditions**, and logistical costs like transportation, all play a role in determining the final cost. Understanding these factors helps you budget with a clearer perspective.
Beyond Material Price: Consider Hidden Costs
An accurate budget is not limited to the price of the material itself. Be sure to include additional costs in your calculations. Typically, **transportation costs (5% to 10%)**, **installation and labor (20% to 30%)**, and **ancillary equipment (10% to 15%)** will be added to the total material cost.
Quality Assurance: What Standards and Signs to Look For?
International Standards: The Common Language of Quality
To ensure product quality, pay attention to global standards. **ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials)** standards such as ASTM C177 for thermal conductivity or ASTM E84 for fire resistance, provide precise criteria for product performance. Additionally, **ISO (International Organization for Standardization)** certifications, especially ISO 9001, indicate the manufacturer’s commitment to a quality management system.
How to Recognize Quality in Practice
A product’s quality can be assessed through several key signs: look for valid certifications, ask the supplier to provide laboratory test results, check the supplier’s history and reputation, and ensure there is a valid product warranty. These elements provide peace of mind throughout your project.
Flawless Execution: From Preparation to Safe Installation
Preparation: The Cornerstone of a Successful Installation
Before starting the installation, take the preparation stage seriously. This stage includes a thorough surface inspection to ensure it is clean and smooth, **final dimension measurements** to prevent errors, and preparing all necessary tools and equipment. Good preparation is half the success of the execution.
Installation: Precision, Skill, and Safety
The installation steps must be carried out with precision and according to the manufacturer’s instructions. For example, when installing rock wool, the process includes precise cutting, **full placement in position** without creating gaps, **fastening with appropriate connectors**, and finally, applying a protective coating. Throughout all these stages, adhering to safety precautions such as using personal protective equipment and ensuring proper ventilation of the work area, is the top priority.
Protecting the Investment: Principles of Maintenance and Repair
Periodic Inspection: Prevention is Better Than Cure
To maintain optimal insulation performance in the long term, periodic inspections are essential. During these inspections, carefully check the physical condition of the insulation, any signs of wear or damage, the thermal performance of the system, and the stability of the connections to address potential problems before they become serious.
When Should Insulation Be Repaired or Replaced?
Some signs are red flags indicating the need for insulation repair or replacement. A noticeable decrease in thermal performance, observation of extensive physical damage, penetration and moisture absorption, or reaching the end of the service life defined by the manufacturer, are all signs that should be taken seriously.
Success Stories: Real Results in the Real World
Case Study 1: Transformation in a Power Plant
Challenge: A power plant was facing severe heat loss from a steam turbine operating at 550°C, leading to increased fuel consumption.
Solution: An engineered solution was implemented using custom turbine jacket insulation designed with a dense rock wool core.
Result: The results were astonishing: a 25% reduction in energy consumption, a 30% increase in equipment lifespan, and a full return on investment in just 18 months.
Case Study 2: Enhancing Safety and Efficiency in a Petrochemical Plant
Challenge: Critical pipelines in a petrochemical unit required simultaneous protection against corrosion and heat loss.
Solution: A smart hybrid system was employed, consisting of advanced thermal insulation and an anti-corrosion coating.
Result: This solution led to a 40% reduction in maintenance costs, a significant increase in operational safety, and improved final product quality due to precise temperature control.
A Look to the Future: Innovations and Upcoming Trends
Game-Changing New Technologies
The future of the insulation industry is tied to the emergence of exciting technologies. Materials like Aerogel with the highest insulating performance and extremely low weight, and nanomaterials that elevate the thermal and mechanical properties of traditional insulations to a new level, are transforming this industry.
Key Trends Shaping the Future
The global market is moving towards more sustainable and intelligent solutions. The increasing demand for green and environmentally friendly insulations, the development of smart materials capable of adapting to environmental conditions, **stricter safety standards**, and the effort to reduce production costs through innovation are the four main trends shaping the future of this industry.
Conclusion
Purchasing insulating materials is a strategic decision that requires careful consideration of various factors. The right choice not only saves costs but also improves the system’s performance and safety.
Key Takeaways:
- Detailed analysis of needs before purchasing
- Choosing a reputable supplier
- Paying attention to quality standards
- Planning for maintenance
About Klevers Aryana
Klevers Aryana company, as the exclusive representative of Klevers Germany in Iran, is a reputable supplier of various insulating materials and fire-resistant fabrics. Leveraging advanced German technology, the company offers a wide range of products, including:
- Jacket thermal insulations
- Rock wool and ceramic fibers
- Fire-resistant blankets and fiberglass meshes
- Passive fire protection insulation
- Fabric expansion joints
For a free consultation and to receive a price quote, contact our experts through the Contact Us page.
Sources:
- Department of Energy – Insulation Materials
- ASTM International Standards
- Rockwool International – Mineral Wool Properties
- Unifrax – Ceramic Fiber Applications
- ISO Standards for Thermal Insulation
- The Refractories Institute
- National Insulation Association
- NUTEC – Industrial Thermal Insulation
- Thermaxx Jackets – Insulation Materials
- Engineering ToolBox – Mineral Wool Properties